Master Data Management

Master Data Management (MDM)
In this blog, we talk about the most important piece of the data jigsaw - Master Data and the management of it using the OpenDataDSL Master Data Management Platform.
What is Master Data?
Master Data is the most important piece of data in the enterprise.
- It is the descriptive information about a particular asset or object.
- It is the central data that connects all other types of data (transactions, timeseries, events etc.)
The purpose of master data is to ensure data integrity, consistency, and accuracy across different systems and processes within an organisation. It acts as a single source of truth that can be shared and accessed by multiple applications and departments. By maintaining high-quality master data, organisations can make informed decisions, improve operational efficiency, enhance customer service, and achieve better business outcomes.
Master Data in OpenDataDSL
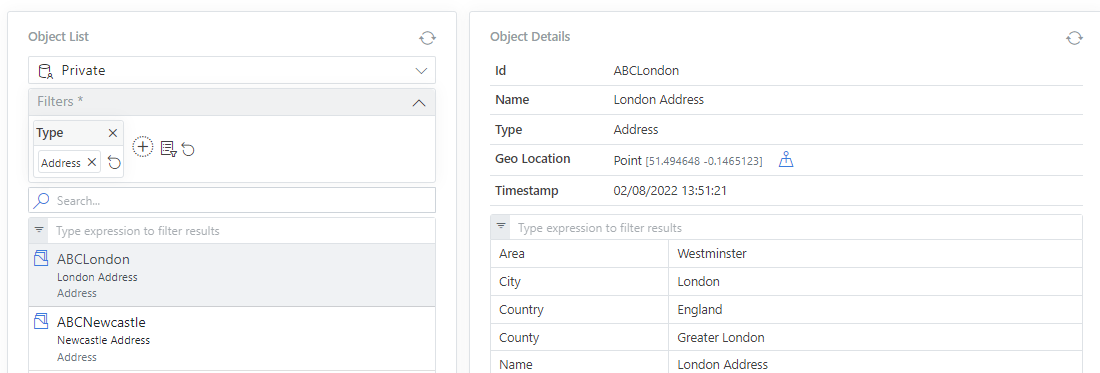
Master Data Attributes
Generally it contains attributes such as:
- Name and Description
Human-readable, easily-understandable summary information about the asset or object
- Identifiers
These are keys which systems use to uniquely identify the asset or object
- Dimensions or Facets
These are categorisation properties that can be used to filter and navigate through the data
- Descriptive Properties
Additional properties or text to provide more details about the asset
It could also include valuable attributes such as:
- Versioning
In order to track changes made to Master Data
- Links
Hyperlinks to the data items that this Master Data represents, such as timeseries, reports etc.
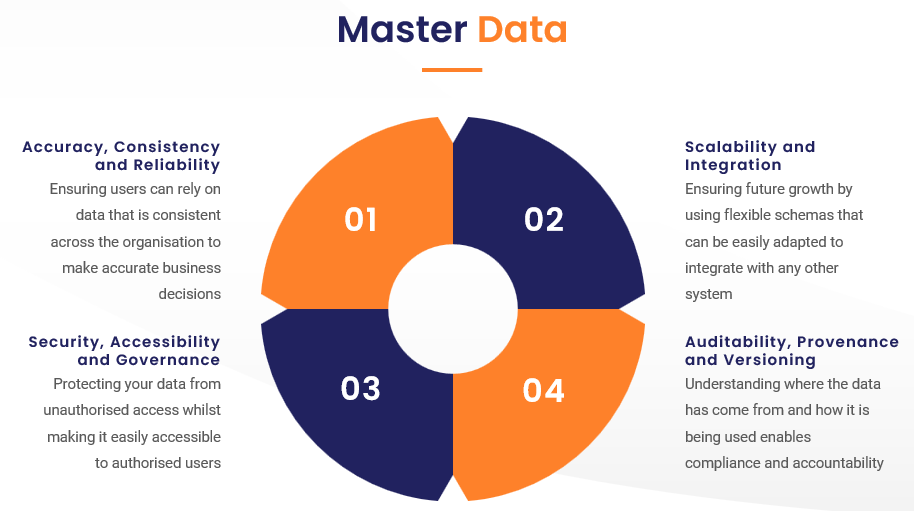
- Accuracy, Consistency and Reliability
Master data should be accurate and reflect the correct and up-to-date information about the entities it represents. Accuracy ensures that the data can be relied upon for making informed decisions and conducting business operations.
Master data should be consistent across different systems, departments, and processes within an organisation. Consistency ensures that everyone is working with the same set of data, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
Master data should maintain data integrity, which means it should be complete, valid, and reliable. It should be free from duplication, inconsistencies, and errors. Data integrity ensures the reliability of the data and its suitability for use in various applications and processes.
- Scalability and Integration
Master data should be scalable to accommodate the growth and changing needs of the organisation. It should be designed in a way that allows for the addition of new entities, attributes, and relationships without significant disruption or loss of data quality.
Master data should be capable of integration with other systems and processes within the organisation. It should support data exchange and synchronisation between different applications and ensure a consistent view of data across the enterprise.
- Security, Accessibility and Governance
Master data should be protected from unauthorised access, manipulation, and loss. It should adhere to data security policies and implement appropriate access controls to safeguard sensitive information.
Master data should be easily accessible to authorised users and systems. It should be available in a consistent format and structure that can be easily understood and used by different applications and processes across the organisation.
Master data should be governed by well-defined data governance policies and procedures. Data governance ensures that there are clear rules and processes in place for creating, managing, and updating master data. It helps maintain data quality, security, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Auditability, Provenance and Versioning
Master data should have an audit trail that allows tracking and monitoring of changes made to the data. It enables accountability, traceability, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Provenance helps us understand who is using the data and how it is being used.
Versioning is the what, when, who and why of changes made to master data are captured in versions and audit logs. Versions and audit logs should include meta-data that covers all those questions:
- Change Details:
The information about what was changed
- Timestamp:
The time and date of when the change was made
- User Id:
The user who made the change
- Reason:
An audit entry specifying why the change was made
- Change Details:
What is Master Data Management?
Master Data Management is the process of creating and maintaining master data.
Master Data Management (MDM) is typically supported by dedicated software tools and technologies that provide capabilities for data integration, data quality management, data governance, and data synchronisation. These tools assist in managing master data throughout its lifecycle, from data creation and cleansing to ongoing maintenance and data governance.
By implementing MDM, organisations can achieve a unified and accurate view of their master data, leading to improved decision-making, operational efficiency, and customer experience. It enables organisations to leverage their data as a strategic asset and supports initiatives such as digital transformation, analytics, and data-driven innovation.
OpenDataDSL Master Data Management
The OpenDataDSL platform allows you to easily implement Master Data Management in the cloud.
The OpenDataDSL platform provides all the features of master data discussed above along with the ability to integrate with more complex data types, such as:
- Events or Transactions
Events are 'point-in-time' information about something that has been recorded
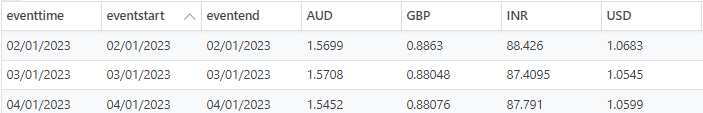
- Timeseries
Timeseries data is a collection of events ordered by time and aligned to a specific calendar
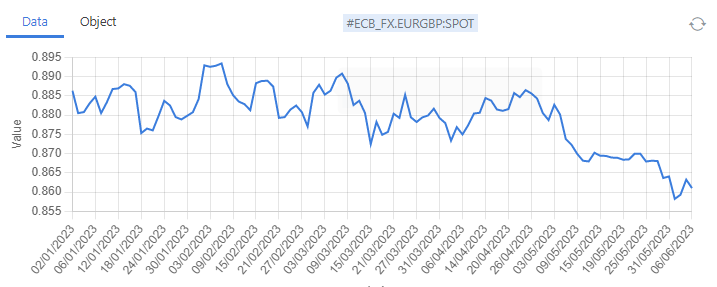
- Forward Curves
Forward curves are used for recording prices to deliver goods at a future delivery date along with forecasts and other financial instruments
- Matrices
Matrices are used to store statistical measurements such as correlations and covariances
Conclusion
Master Data Management enables organisations to establish a solid foundation of high-quality master data, ensuring data consistency, integrity, and accessibility. It empowers businesses to leverage their data as a strategic asset and drive better business outcomes.
Next steps
Do you want to see this in action and see how you can benefit from OpenDataDSL?
Fill out the form below, we will contact you to arrange a personally tailored demo.

How about a demo?
Our team is here to find the right solution for you, contact us to see this in action.
Fill out your details below and somebody will be in contact with you very shortly.
More information or free trial?
Tell us about your project, and we can let you know how we can help.
Contact us at info@opendatadsl.com
